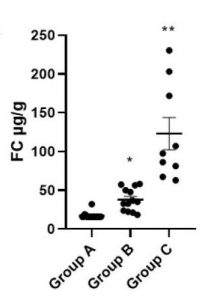
Patients with colonic IBD who have recently started therapy using agents such as biologics, JAK inhibitors, or azathioprine, should undergo endoscopy to assess the efficacy of treatment after 6–12 months. However, other tools could be used (eg, faecal calprotectin or bowel ultrasound). As such, endoscopic monitoring may not be essential.
A further risk is missed detection of early post-operative recurrence in patients with Crohn’s disease after ileocolonic surgery. Ileocolonoscopy to check the anastomosis site should be performed within 6–12 months after the surgery. Indirect tools, such as faecal calprotectin, bowel ultrasound, and magnetic resonance enterography, have been shown to be useful in disease monitoring and may help avoid endoscopy.
Click Here to Find Out More